The Primary Mechanisms to Form Precipitation Are the
Cloud droplets can grow and produce precipitation including rain snow sleet freezing rain and hail which is the primary mechanism for transporting water from the atmosphere back to the Earths surface. Saturation is the first step in the formation of precipitation ie.

Replica Plating Or Stamping Indirect Selection Nutrient Medical School Pre Med
By coming into contact with a cold object such as ground mountains.
. It means that some special processes are working in a cloud from which precipitation falls. 5 collision-coalescence process only. Under ideal conditions seeding may enhance precipitation.
This salt then precipitates out of solution. Water vapor condenses into liquid water droplets forming clouds. In this lesson explore the mechanisms that cause precipitation.
Mechanisms of producing precipitation include convective stratiform and orographic rainfall. Necessary condition to the formation of precipitation is that the air becomes saturated withwater vapor. In order to have this in the atmosphere you have to first have 100 relative humidity or close to it.
Convective processes involve strong vertical motions that can cause the overturning of the atmosphere in that location within an hour and cause heavy precipitation while stratiform processes involve weaker upward motions and less intense precipitation. Two primary methods are used to trigger the precipitation process. Ice Phase Processes Wegener-Bergeron-Findeisen Collision-Coalescence Process.
Continuous episode of heavy snow and winds exceeding 56 kmhr 35 mph cloud seeding. The primary mechanism for precipitation formation outside of the tropics. All forms of precipitation are the result of the water cycle or the movement of water between the earth and the atmosphere.
This process involves the coexistence of ice crystals and supercooled water droplets. A solution with a large positive value of RSS has a high rate of nucleation and produces a precipitate with many small particles. In warm clouds where all of the cloud droplets are liquid the collision-coalescence process is the primary mechanism responsible for producing precipitation.
Saturation is typically quantified by relative humidity. Relative humidity is the percentage of water vapour in the air as a percentage of the amount of water vapour that that air can hold at its present temperature. Although moisture is always present in the atmosphere but it is condensed only when air is cooled and saturated with some water vapors.
The primary mechanisms to form precipitation are the collision-coalescence and Bergeron processes The precipitation in form of liquid water droplets that forms by condensation or by melting ice crystals as they pass through a warm layer of the atmosphere is. The relative humidity RH is defined as. Dry ice is used to lower cloud temperature to a freezing point in order to stimulate ice crystal production leading to the Bergeron process.
The following is a common. The most important mechanism is uplift of air as air rises its pressure decreases it expands and cools down. This is thought to be the case especially over tropical.
In cooler airmasses precipitation rain or snow usually occurs in large cloud systems associated with low pressure zones. Precipitation is the process through which water vapor condenses and falls from the sky. A precipitation reaction can occur when two solutions containing different salts are mixed and a cationanion pair in the resulting combined solution forms an insoluble salt.
When the RSS is small precipitation is more likely to occur by particle growth than by nucleation. We will discuss two primary rain formation theories. When precipitation falls over the land surface it follows various routes in its subsequent paths.
It is necessary but notsufficient. The primary mechanisms to form precipitation are the A collision-coalescence B Bergeron and Wegener. The numerator of Equation 8212 Q S is a measure of the solutes supersaturation.
Its ability to hold water is reduced to a certain point. Convective uplift orographic uplift and. Precipitation is the liquid or frozen water that falls to the ground and is formed from the condensation of water vapor.
Within the clouds the water vapor changes to ice crystals by. These ice crystals coalesce join together and become heavy enough to be pulled down by gravity as precipitation and do not melt before they hit the ground as a snowflake. Precipitation is often classified according to the factor responsible for lifting of air to higher altitudes.
Collision Coalescence Process. On Earth the heat from the sun causes surface water to evaporate or. Usually mechanism by which air is cooled to cause precipitation is the lifting of air mass.
In order for precipitation to form you first need liquid water or ice. 2Bergeron and Wegener processes. These low pressure zones usually form along the boundary between warm and cold air masses where the flow of air around the low pressure causes large areas of weak rising motion as air from the warmer air mass flows up and.
Precipitation occurs only when the cloud droplets or ice crystals grow to such a size that it can overcome the updrafts in the atmosphere. Silver iodide initiates the Bergeron process by directly acting as freezing nuclei. Growing clouds are sustained by upward air currents which may vary in strength from a few centimetres per second to several metres per second.
Learn about precipitation forming processes and explore the growth of water. The primary mechanisms to form precipitation are the 1 Bergeron process only. 4 Findeisen and Wegener processes.
3 collision-coalescence and Bergeron processes. There are two processes which can explain these mechanisms. Considerable growth of the cloud droplets with falling speeds of only about 1 cm or 04 inch per second is therefore necessary if they are to fall through the cloud survive evaporation in the.
Mechanisms of precipitation release.

Lifting Mechanisms North Carolina Climate Office

8 2 Precipitation Gravimetry Chemistry Libretexts
Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes Atmospheric Processes And Phenomenon

The Glyoxylate Cycle Also Known As The Glyoxylate Bypass Or Glyoxylate Download Scientific Diagram Acetyl Coa Chemistry Cycling
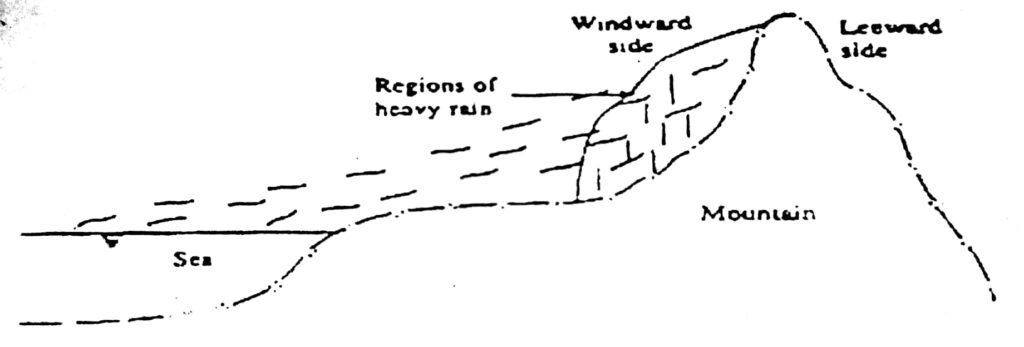
Precipitation Its Causes Classification And Types Cement Concrete

Lifting Mechanisms North Carolina Climate Office

Animal Adaptations Matching Defense Mechanisms Animal Adaptations Defense Mechanisms Adaptations
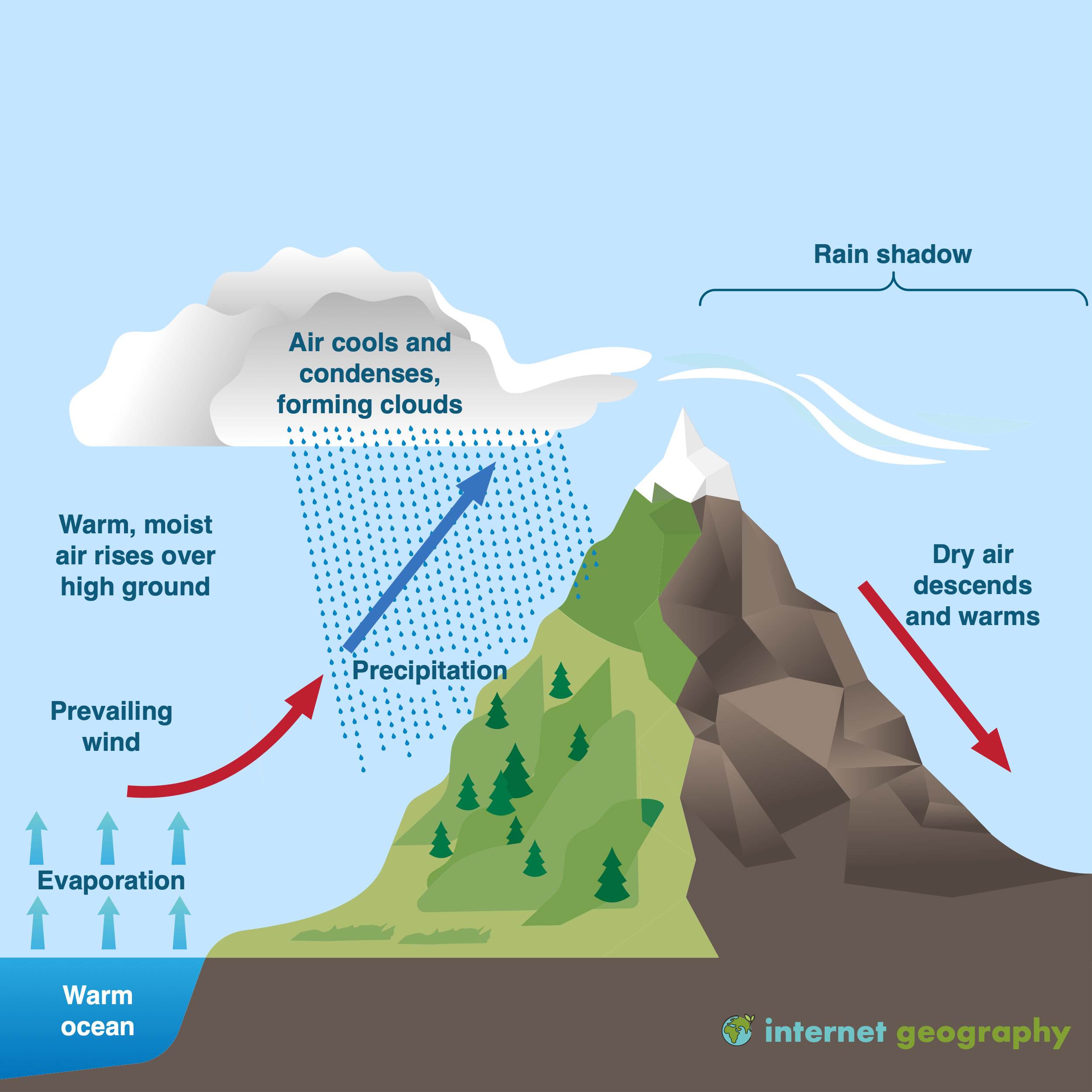
What Is Relief Rainfall Internet Geography
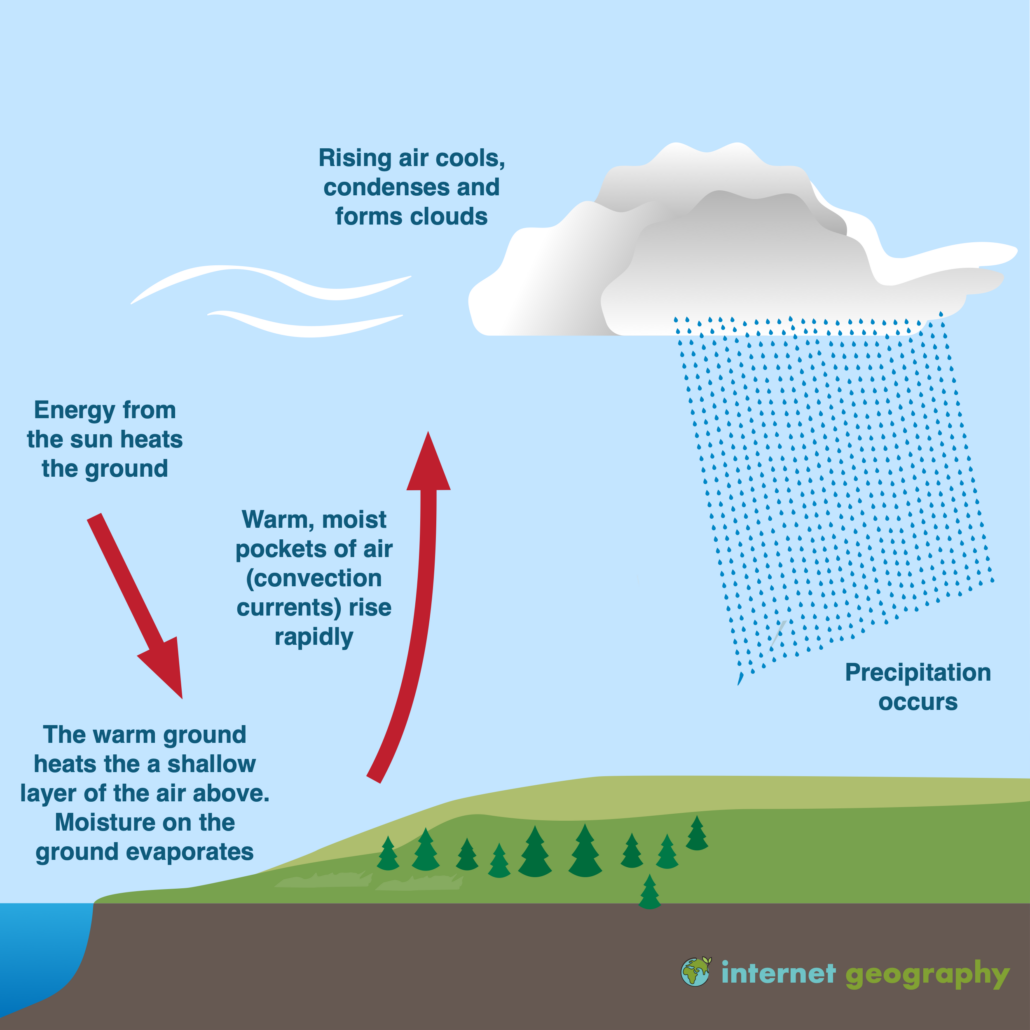
What Is Convectional Rainfall Internet Geography
Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes Atmospheric Processes And Phenomenon

Lifting Mechanisms North Carolina Climate Office

Hydrological Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Biology 2108 Biology Plants Teaching Plants Science Biology

The Spliceosome Schematic Diagram Of The Steps Of Spliceosome Assembly Download Scientific Diagram Medical University Biochemistry Diagram

What Is Precipitation And What Are Different Types Of Precipitation Earth Eclipse

Definition And Measurement Of Colloids Water Treatment Macromolecules Solubility

Lifting Mechanisms North Carolina Climate Office

Hydrological Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Precipitation Its Causes Classification And Types Cement Concrete
Comments
Post a Comment